Museum Exhibit: Sustainability in Chaos
Jurors Helen Hiebert and Eileen Wallace invited twenty-nine paper artists to demonstrate their insights as artists in the chaos of today's life and how they transform chaos into a vision of what is possible. Through the medium of paper with its boundless style, sustainability, and conceptual framework, the featured artists share their responses to chaos and demonstrate how the arts and sustainability can elevate inspiration and leave a lasting impression on communities.
Photochemistry and a New Catalyst Could Make Fertilizer More Sustainable
Dec 22, 2023 — Atlanta, GA
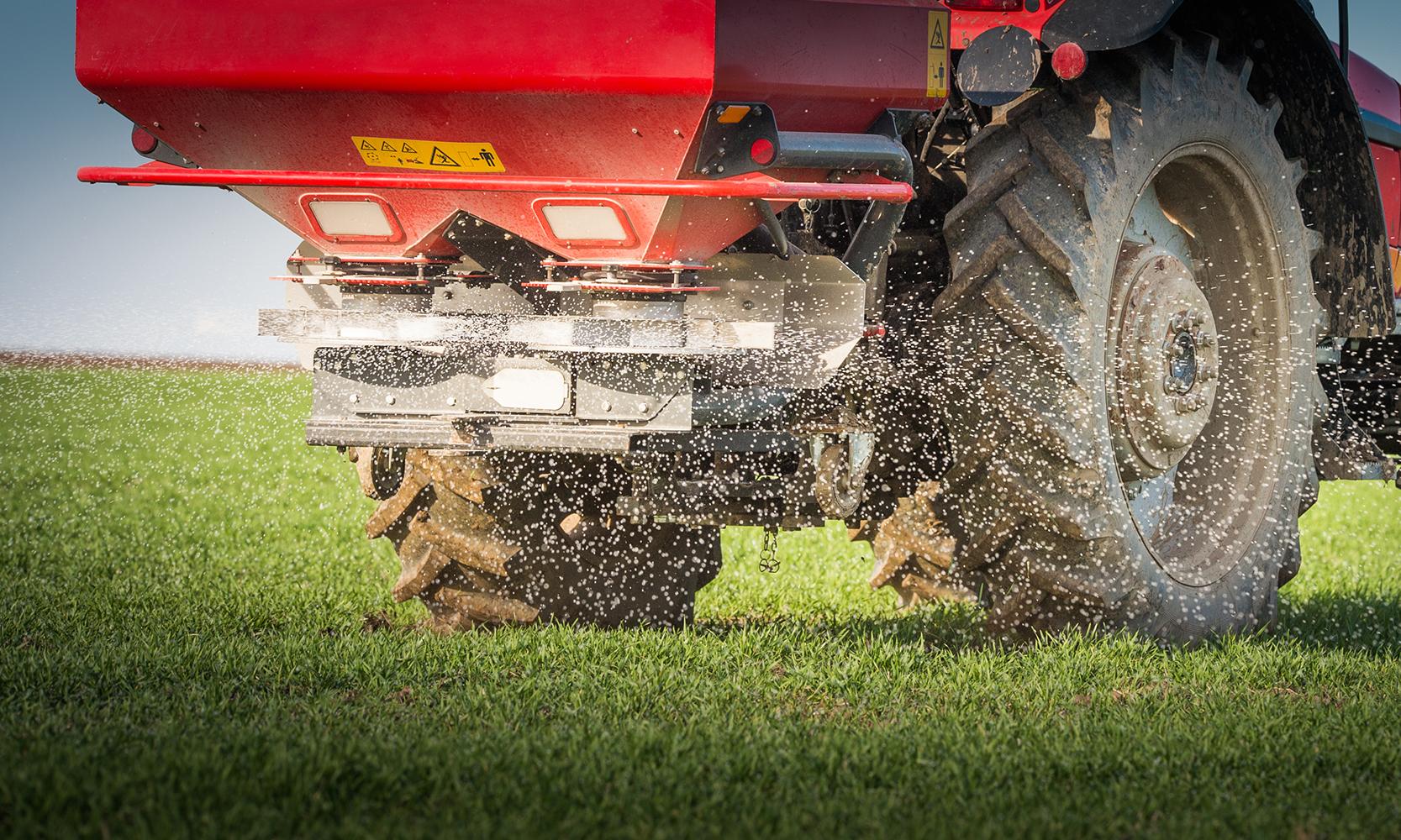

Georgia Tech engineers are working to make fertilizer more sustainable — from production to productive reuse of the runoff after application — and a pair of new studies is offering promising avenues at both ends of the process.
In one paper, researchers have unraveled how nitrogen, water, carbon, and light can interact with a catalyst to produce ammonia at ambient temperature and pressure, a much less energy-intensive approach than current practice. The second paper describes a stable catalyst able to convert waste fertilizer back into nonpolluting nitrogen that could one day be used to make new fertilizer.
Significant work remains on both processes, but the senior author on the papers, Marta Hatzell, said they’re a step toward a more sustainable cycle that still meets the needs of a growing worldwide population.
“We often think it would be nice not to have to use synthetic fertilizers for agriculture, but that’s not realistic in the near term considering how much plant growth is dependent on synthetic fertilizers and how much food the world’s population needs,” said Hatzell, associate professor in the George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering. “The idea is that maybe one day you could manufacture, capture, and recycle fertilizer on site."
Joshua Stewart
College of Engineering
Why Your Scissors Glide (or Don't) When You're Wrapping Presents
Dec 21, 2023 — Atlanta, GA

Wrapping Presents
In the hustle and bustle of the holidays, a moment of transcendence can happen as you wrap presents: scissors in hand, cutting a piece of wrapping paper from the roll, the blades hit their stride and slide from end to end.
Why is it sometimes the scissors glide, and other times the paper tears a dozen times? Christopher Luettgen says it all has to do with paper quality.
“Good wrapping paper is going to have a prettier surface. It may even have a textured surface, maybe embossed or more three dimensional,” said Luettgen, a professor of the practice with the Renewable Bioproducts Institute and an expert on paper.
High-quality wrapping paper is made from softwood pulp — in particular, the strongest pulp you could make is southern pine softwood.
“The really good paper starts with softwood fiber,” he said. “Softwood kraft in particular — ‘kraft’ being an old German word for ‘strong.’ It’s going to be stiffer and stronger in multiple directions. Then it gets coated so you get a nice clay coating on the surface, which will smooth the surface to get it beautifully printed. When you come across weak paper that wants to tear very easily, it is often made with mechanical fibers.”
So, if you want the glide, you want good paper. When might it be worth skimping on quality?
“If you’ve got a big job, like you want to wrap a TV or a large game or something like that, you don’t want to spend a lot of money on the high-end wrapping papers. It’s going to get torn up pretty fast. That’s when you might go with a cheaper, thinner brand.”
Of course, as Luettgen notes, you can’t tear the paper in the store, but looking for a thicker paper is a good start. The thicker paper will also give your presents a more refined look under the tree.
“Let’s say you’re giving a book to somebody. You want nice tight corners. You want good creasing. You really want to make it showy.”
Why, then, does Santa sometimes not wrap his presents? Luettgen believes it’s all a matter of resources leading up to Christmas Eve.
“If he has enough help at his studio, I would think that he’s going to get all of your presents wrapped. But if he’s rushed, with bad weather for instance, he may have to come down the chimney with the presents unwrapped, but they’ll be under the tree.”
Institute Communications
Seminar - Department of Energy Zero Carbon Energy: Progress to Net Zero
Join us on January 17th at 9am at 1128 Petit Institute for Bioscience and Bioengineering (IBB) for a seminar on "Department of Energy Zero Carbon Energy: Progress to Net Zero" by John
SEI/RBI Initiative Lead Profile: Matthew Realff
Dec 13, 2023 — Atlanta, GA

Portrait of Matthew Realff
Matthew Realff, professor and David Wang Sr. Fellow in the School of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, leads the Circular Carbon Economy Research Initiative in the Strategic Energy Institute and the Next Generation Refineries Research Initiative in the Renewable Bioproducts Institute at Georgia Tech. Realff co-directs the Direct Air Capture Center (DirACC), which coordinates research across the Institute aimed at the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Realff’s broad research interests are in the areas of process design, simulation, and scheduling. His current research is focused on the design and operation of processes that minimize waste production by recovery of useful products from waste streams, and the design of processes based on biomass inputs. In particular, he is interested in carbon capture processes both from flue gas and dilute capture from air as well as the analysis and design of processes that use biomass. Below is a brief Q&A with Realff where he discusses his research focus areas and how it influences the circular carbon economy research initiatives at Georgia Tech.
- What is your field of expertise and at what point in your life did you first become interested in this area?
My background is in chemical engineering with a focus on process design and simulation, which is part of the field of process systems engineering. I have been interested in this general topic since first setting foot on the campus of Imperial College London in 1982, and subsequently pursued it as my Ph.D. topic. I first started thinking about direct air capture of CO2 in 2011 and about circular carbon from CO2 in 2016.
- What questions or challenges sparked your current energy research? What are the big issues facing your research area right now?
I believe that managing CO2 emissions will be the biggest challenge of the next 50 to 100 years. We will need to have negative emissions, as we are emitting too much, and pulling CO2 directly out of the atmosphere will be required because we are going to continue to emit. Creating technological solutions to provide negative emissions is one of the biggest challenges, as they need to be cost-effective and environmentally and socially less damaging than the emissions they capture. The biggest issue facing my research is understanding the phenomena that are involved in direct air capture and translating that understanding into engineered systems that are low-cost, have low environmental impact, and are socially beneficial.
- What interests you the most leading the research initiative on circular carbon economy? Why is your initiative important to the development of Georgia Tech’s energy research strategy?
The circular carbon economy is a systems problem in the broadest sense. This means that we must embrace a multidisciplinary approach to synthesize effective solutions. I want to emphasize the word “effective” here — we must embrace a wide range of measures of performance from energy efficiency to social justice because without improving along many dimensions we will be unlikely to be successful. It is this multidimensional, multidisciplinary research effort that interests me, as I love to find ways to bring people together to synthesize different knowledge into effective solutions. Georgia Tech is a world leader in direct air capture technology — as demonstrated by our new Direct Air Capture Center (DirACC). Our advances in this topic area can provide a base from which to develop approaches to carbon utilization, and other research efforts in electro, bio, and thermo chemical technologies can enable closed pathways using carbon as an energy carrier.
- What are the broader global and social benefits of the research you and your team conduct on circular carbon economy?
One vision for our energy and material systems is to have a much greater local production and consumption of energy using renewable resources. A circular carbon economy based on CO2 from the air; water from local sources including the air; and solar, wind, or biomass-based energy could be local and would have many transactions between local parties. This could serve to not only reduce global emissions but also to provide more opportunities for communities to benefit from the production of energy as opposed to having many transactions that transfer money outside of the community.
- What are your plans for engaging a wider Georgia Tech faculty pool with the broader energy community?
DirACC is one way we hope to connect faculty to the ecosystem of companies that are developing and deploying DAC technology. We hope that the challenges that these companies are articulating can be translated into research topics for the faculty affiliated with the center. The Department of Energy’s efforts to establish the DAC Hubs provides us with other opportunities to engage faculty around social and environmental justice issues associated with deploying energy technologies such as direct air capture. I hope that faculty will see themselves participating in these efforts and reach out to be included in the network of researchers on these topics.
- What are your hobbies?
My main hobby is playing a card game called Magic: The Gathering. I have played this since 1994 and have enjoyed many friendships formed as a dueling wizard. I also enjoy reading, particularly science fiction and steampunk literature, as well as history.
- Who has influenced you the most?
Professor Roger Sargent at Imperial College was one of the founders of the field of process systems engineering. His speech on elevation to the position of professor at Imperial in 1963 has had a profound impact on the direction of my research and educational activities.
Priya Devarajan || Research Communications Program Manager SEI || RBI
Six Named to National Academy of Inventors
Dec 12, 2023 — Atlanta, GA
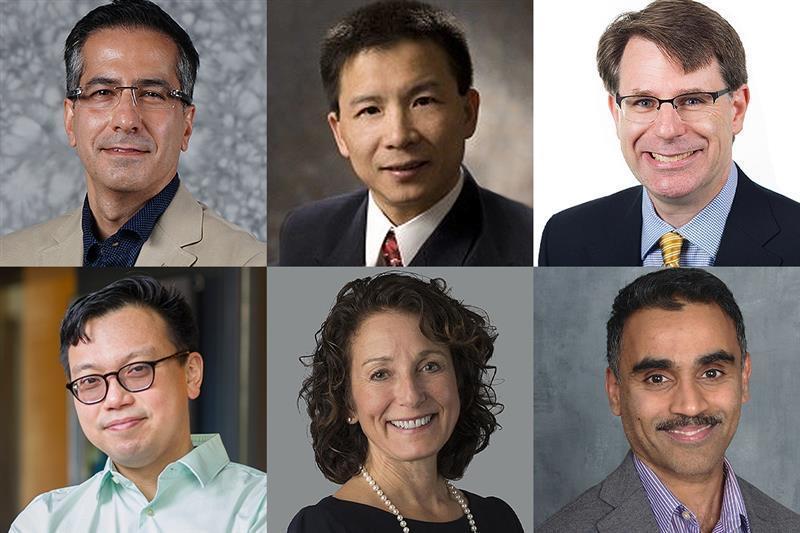

Six Georgia Tech College of Engineering faculty members are among the National Academy of Inventors (NAI) 2023 Class of Fellows. The honor is the highest professional distinction awarded solely to inventors.
No other university or organization in the world has more honorees this year than Georgia Tech. The group of six holds more than 200 patents.
- Farrokh Ayazi, electrical and computer engineering
- Maohong Fan, civil and environmental engineering
- Christopher Jones, chemical and biomolecular engineering
- Wilbur Lam, biomedical engineering
- Susan Margulies, biomedical engineering
- Karthikeyan Sundaresan, electrical and computer engineering
The Georgia Tech engineers are among 162 worldwide inventors honored in 2023. According to the NAI, “their work spans across disciplines and exemplifies their dedication and inspiration to translating research into commercial technologies that benefit society.”
The 2023 class will be honored in June at the NAI annual meeting.
Jason Maderer, College of Engineering Director of Communications
jason.maderer@coe.gatech.edu
RBI Releases 2024-25 Fellowship Request for Proposals
Nov 27, 2023 — Atlanta, GA

The Renewable Bioproducts Institute (RBI) at Georgia Tech benefits from a substantial endowment that is invested to advance the evolving science and technology needs of the bioproducts industry and emerging bioeconomy through graduate research. The endowment over the years has supported more than 1,500 engineers and scientists and a leading body of scientific research. RBI has released the Request For Proposals (RFP) for the annual year 2024-25 fellowships. Proposals are due on Feb. 1, 2024. The RFP document describing the application process and several important changes for this year can be found at 2024-25 RFP Proposals.
The principal mission of RBI is to incubate and develop interdisciplinary teams of researchers that can establish thought leadership through new bioproduct research directions. Our focus is on pre-competitive, use-inspired research with a technical, economic, or policy focus. All supported work needs to address an aspect of bioproducts and the developing bioeconomy. The RBI Fellowship supports this mission by promoting two objectives:
(1) Helping teams of faculty to establish new concepts, publish early results, and develop competitive federal, industry, or foundation proposals in the future.
(2) Training a diverse group of graduate-level professionals who can support the evolving bioproducts R&D workforce.
***NEW PROGRAM CHANGES***
- Along with Graduate Research Assistant (GRA) stipend and tuition support, RBI will provide $1,000 of materials and supplies funding or a $1,000 credit toward the use of RBI’s analytical facilities.
- The fellowship was formerly called the PSE (Paper Science and Engineering Fellowship). It has been renamed as the RBI Fellowship.
- The fellowship minor requirement has been changed from 12 hours to nine hours. The minor will consist of two core courses and one elective, described here. For students outside of the College of Sciences or College of Engineering, an alternative set of courses can be considered.
- Awards can support GRAs from any school within Georgia Tech and can be advised by teams consisting of faculty from any Georgia Tech school, although the relevance of the disciplines included must be clear.
Priya Devarajan || RBI Communications Program Manager
Georgia Tech Authors Celebration 2024
Georgia Tech faculty and staff are invited to join the Office of the Executive Vice President for Research and the Library for the annual Georgia Tech Authors Celebration.
This event celebrates Georgia Tech book publications, showcasing the range and depth of scholarship on our campus. The 2024 event honors authors and editors who have published books between January 2022 and December 2023.
A Day’s Work at the RBI Chemical Analysis Lab
Nov 09, 2023 — Atlanta, GA
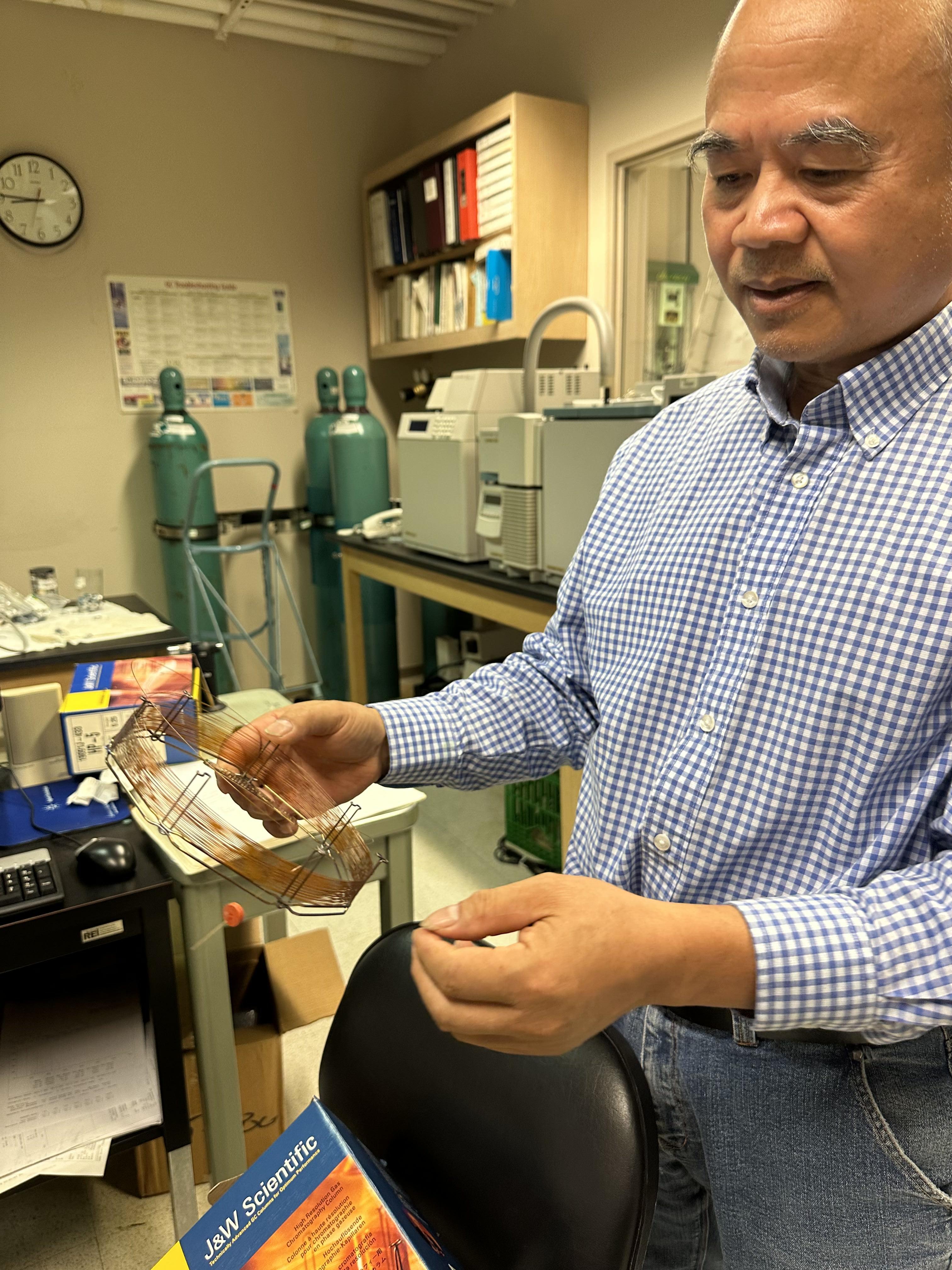
Rallming Yang, Senior Research Scientist and head of the Chemical Analysis Lab explains how FTIR Spectrometer works, at the RBI Chemical Analysis Lab
Providing research testing services to both internal and external stakeholders is an integral function of the Renewable Bioproducts Institute (RBI). These services include chemical analysis; corrosion; paper, board and box testing; pulp analysis; and pulp recovery analysis. Established over 25 years ago, RBI’s testing services are well-known in the industry for their quality and customer service. RBI is one of the ten interdisciplinary research institutes at Georgia Tech that champions innovation in converting biomass into value-added products, developing advanced chemical and bio-based refining technologies, and advancing excellence in manufacturing processes.
The RBI research testing services is a team of professional scientists and engineers who work together to provide information and offer solutions required by a manufacturers and users of biomass products, as well as Georgia Tech faculty and students engaged in research on campus. The multidisciplinary capabilities of the team make them uniquely qualified to address customers' technical needs in the areas of process and product development, and quality control. Where appropriate, the team involves RBI faculty and other staff experts to arrive at the best possible solution for their customers and users.
In this article, we will focus on a day’s work with the chemical analysis team. Headed by Rallming Yang, senior research scientist at RBI, the team is equipped to follow the Technical Association of the Paper and Pulp industry (TAPPI) standard of testing, which only a small number of labs in the country can do, and has also developed some of its own internal protocols. Yang leads two specific characterization programs within RBI: (1) the pulping and bleaching analysis, paper recycling, and recovery lab, and (2) the chemical analysis lab.
The chemical analysis team is busy year-round with research projects and testing services. In addition, during the Spring semester, the team also provides support to a paper science laboratory course for undergraduate and graduate students. In the recent times, chemical analysis of black liquor from pulp mills has kept the team busy with more than 30 projects completed by the team over three months for various industry customers. Currently, black liquor analysis continues to account for over 50% of the workload of the lab.
Black Liquor (BL) is a byproduct of a wood pulping and is released when cellulose fibers are separated from wood chips. BL contains lignin, which is used as a biofuel within the mill, and several other chemicals that are recovered and reused. In most pulp mills, nearly 50-70% of BL is converted into a convenient source of fuel or energy. Due to the important role played by black liquor in a paper mill, it needs to be tested regularly to ensure consistency in composition. The RBI chemical analysis lab gets BL samples from a pulp mill, who contact the lab by email to get their testing request into the queue. The process involved in the testing is very intense and has multiple steps that need to be carefully administered.
In the first step, inorganic elements in BL are identified by digesting it in a precise mixture of acids and filtering the mixture. The filtrate is introduced into an Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) Emission Spectrometer that can identify more than 70 different inorganic elements and compounds like sulfur, potassium, sodium, iron, calcium, etc. The next step involves identifying the proportion of anions like sulfate, chloride, thiosulfate. In this step, BL is diluted to a specific level and analyzed using a method called Capillary Ion Electrophoresis (CIE).
The next step involves analyzing BL for organic substances using two methods – gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC/MS) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry (FTIR). For organic substances with a lower molecular weight of less than 600 Daltons (Da), GC/MS is employed where the gas chromatography separates the chemical mixture, and the mass spectrometry identifies each of the components.
The final step is to identify organic substances and polymers with higher molecular weights. For example, lignin is one of the main polymers in BL with a molecular weight higher than 600 Da. FTIR is used for testing during this step. Based on vibrations within each molecule, an FTIR spectrum allows identification of molecular groups within lignin. The equipment then uses a computer to identify the substances by comparing the sample spectrum with a built-in library. The RBI team provides detailed lab reports that is used by the pulp mill to adjust their operating parameters for trouble-free operations.
In addition to the chemical analysis of byproducts like black liquor and other chemical compounds, Rallming Yang’s team also conducts studies on pulping and bleaching, repulping, and fiber characterizations.
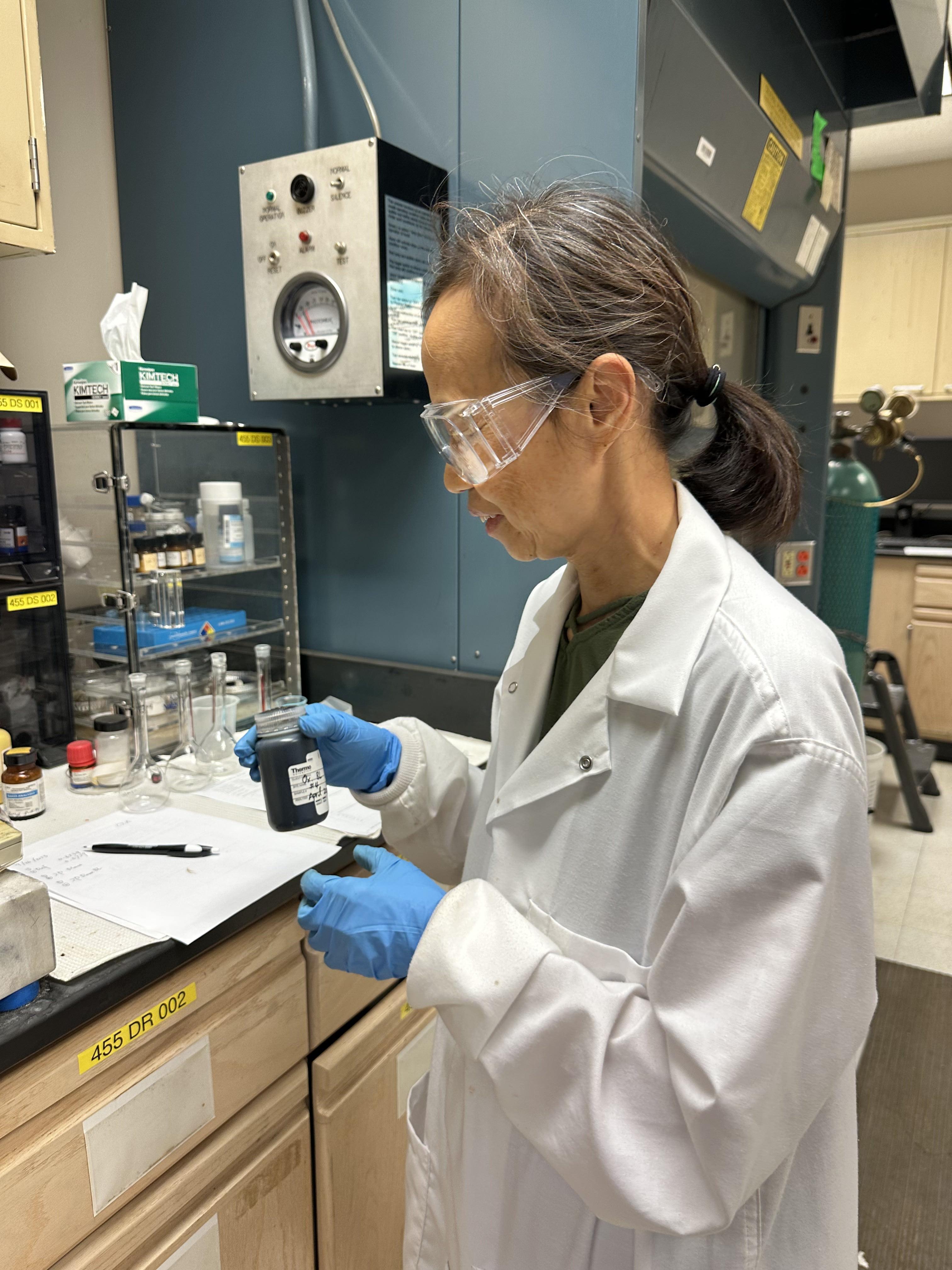

Xiaoyan Zeng, Research Scientist at RBI preparing black liquor for identifying anions
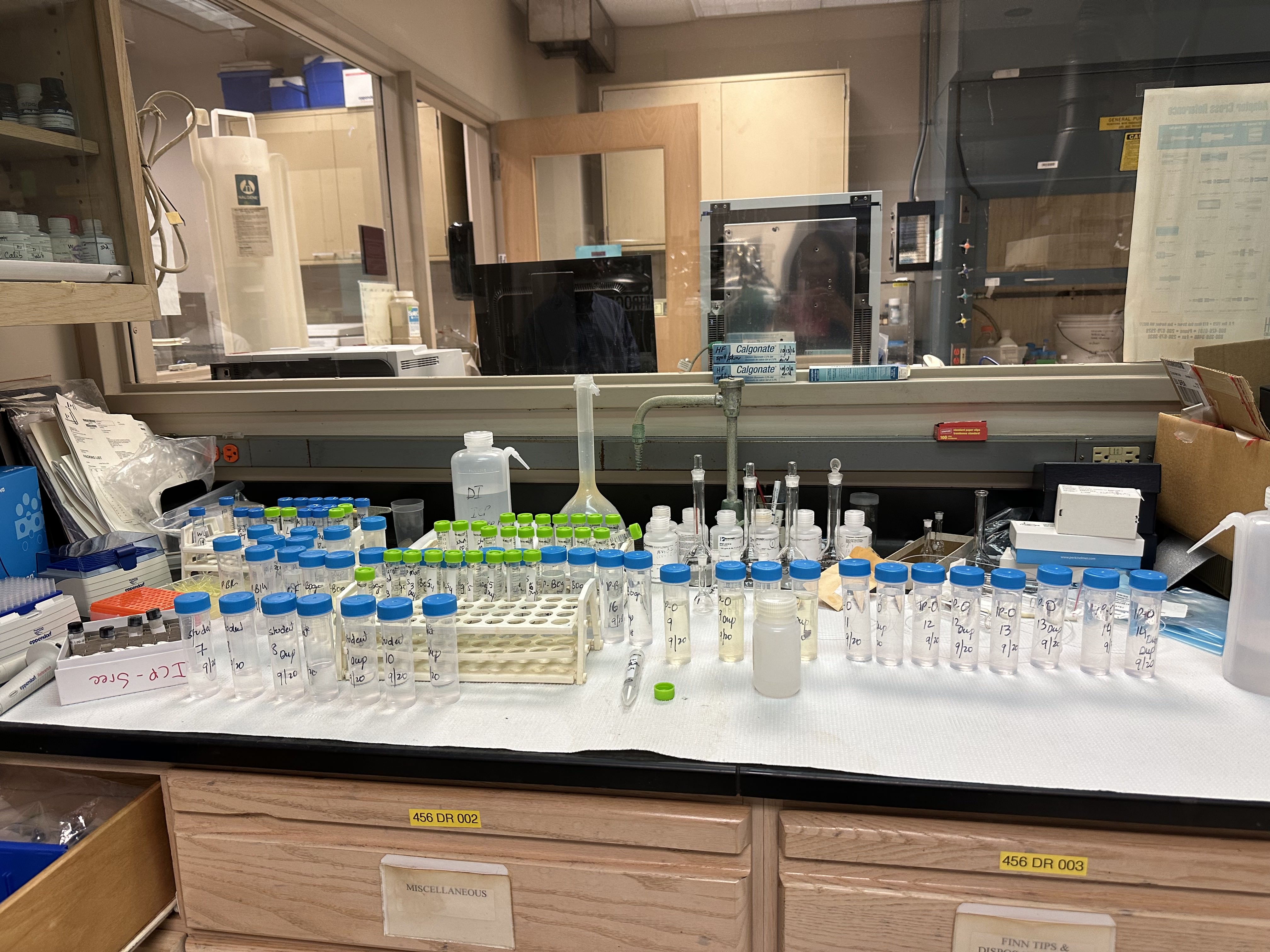

Diluted black liquor ready for testing
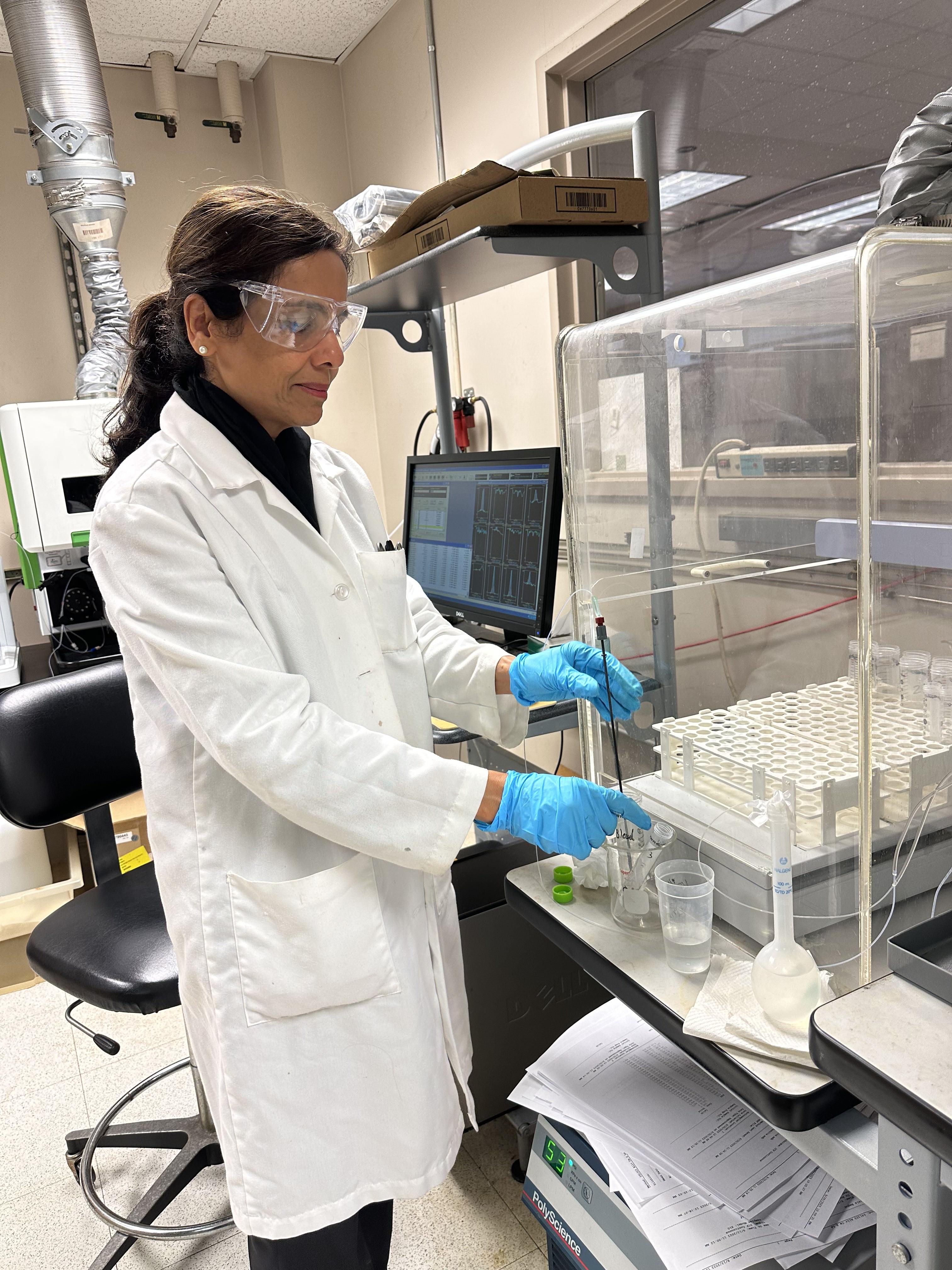

Tabassum Shah, Research Coordinator at RBI, tests black liquor using ICP Emission Spectrometer
Priya Devarajan || Research Communications Program Manager, RBI
Georgia Tech Hosts 2023 RCE Americas Meeting
Oct 20, 2023 — Atlanta, GA

The Georgia Tech campus recently served as host to the 2023 RCE Americas Regional Meeting. From September 26 – 29, students, academics, and working professionals from around the Americas gathered to share their diverse perspectives and experiences, and delved into the discourse of sustainability. Participants attended panel sessions, presentations, site visits, and workshops (one of which was student led) over the three-day meeting, offering their unique viewpoints on how sustainability plays a role in their work and academic careers.
RCE Greater Atlanta was acknowledged by the United Nations University (UNU) on December 18, 2017, as a Regional Centre of Expertise on Education for Sustainable Development. RCE Greater Atlanta is one of over 190 RCEs recognized worldwide as part of the UNU RCE network. RCEs support multi-stakeholder implementation of the U.N. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) at the regional level, through education and training.
RCE Greater Atlanta is committed to leveraging educational resources for regional implementation of the SDGs, with a focus on equity and justice, building on Atlanta’s history as the home of the Civil Rights Movement. RCE Greater Atlanta members, representing all sectors of community, business, government, and civil society, contribute to the creation of an inclusive and collaborative community that advances SDG knowledge and action, and nurtures strong youth leadership by harnessing higher education capacity and knowledge for regional benefit.
Among the speakers were Keisuke Midori, section chief from the Ministry of the Environment of Japan; Jenny Hirsch, senior director of the Georgia Tech Center for Sustainable Communities Research and Education, representing RCE Greater Atlanta; and Georgia Tech President Ángel Cabrera. Several of the speakers traveled or participated virtually from around the United States, as well as from places as far-flung as Mexico, Puerto Rico, Canada, Peru, and Columbia. Atlanta was also well represented with participants and speakers from many area colleges and universities including Morehouse School of Medicine, Kennesaw State University, and Georgia Gwinnett College. A wide range of topics were presented such as “Youth Initiatives at Assateague Island,” “Energy Equity: Advancing SDG 7 Affordable and Clean Energy Through Community-University Partnerships,” and “Young Leaders of the Earth Charter at RCE Bogota.”
Several Georgia Tech students were in attendance and have offered their perspectives on the event. Lakshya Sharma, a master’s student in Human Computer Interaction and the student coordination manager for RCE Greater Atlanta, says, “The conference provided people coming from a wide variety of backgrounds an opportunity to present views, opinions, and talk about differences. I was given the responsibility to lead one of these sessions, where we discussed how important local community action is and how these actions can be made more efficient, inclusive, and effective. Participating in these discussions gave me a fresh perspective on things and made me explore new ways to solve problems, which I can now implement as a professional.”
Perrin Brady, who is studying History, Technology, and Society at Georgia Tech and serving as a student engagement coordinator for RCE Greater Atlanta, said, “I was able to raise questions to the room that I struggle with as a young person, like how to navigate possible conflict between requiring fast climate solutions and needing equitable/sustainable solutions that take time and consideration. People's answers gave me hope for future impacts I could make.”
Julie Chen, another student engagement coordinator, who is studying architecture at Georgia Tech, said, “The range of presentations remains an inspiration, as I was able to witness different RCEs actively involved in unique projects to further the UN SDGs. It was especially heartening to see young students taking the initiative. The RCE Americas Network is a great platform to share these efforts.”
The event was sponsored by Oak Ridge Associated Universities; Kennesaw State University’s Global Education Community Engagement and Outreach; Goethe Zentrum; and several Georgia Tech organizations, namely the Brook Byers Institute for Sustainable Systems, the Renewable Bioproducts Institute, the Strategic Energy Institute, the Atlanta Global Studies Center, and the Ray C. Anderson Center for Sustainable Business with the Drawdown Georgia Business Compact.
The RCE Americas Meeting is an annual event. For more information, see the following links:
Meeting Resources: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1K8XeWuCEXq66TEVZuQQm3X3EzfXQ3zVB?usp=sharing
Presentation Recordings: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpof6N7frRLybc0UW8dhX4A
Kristina Chatfield, Program and Portfolio Manager, Center for Sustainable Communities Research and Education
